This repository contains programs in the C programming language related to Data Structures.
--> C is a general-purpose programming language.
--> It is Procedural Programming language.
--> It has been used to develop operating systems, databases and applications.
--> It is Middle Level Programming language and gives more control to Programmer.
--> GCC stands for GNU C/C++ Compiler.
--> To begin with GCC, visit the official website

--> Download GCC according to the platform being used like Linux, MacOs or Windows.
--> Follow the setup wizard.
--> Write c code in any text editor or IDE and save it with .c extention.
--> Then just open the console and run this command -
gcc filename.c -o Output
--> Filename is the name of the C script file and Output is the name of the output file.
--> After this command is executed, if the code is successfully compiled output file will be saved in the same location as the code file.
--> Once this Output file is executed in command prompt, the output will be displayed.
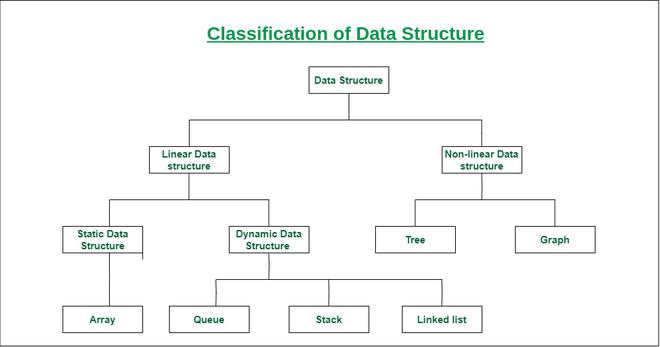
--> A data structure is a storage that is used to store and organize data.
--> It is a way of arranging data on a computer so that it can be accessed and updated efficiently.
Data structure in which data elements are arranged sequentially or linearly, where each element is attached to its previous and next adjacent elements, is called a linear data structure.
--> Static data structure has a fixed memory size.--> It is easier to access the elements in a static data structure.
-->An Array is a sequential collection of elements, of the same data type.
--> They are stored sequentially in memory. An Array is a data structure that holds a similar type of elements.
--> Dynamic data structure: In dynamic data structure, the size is not fixed.
--> It can be randomly updated during the runtime which may be considered efficient concerning the memory (space) complexity of the code.
--> A Queue is a linear data structure that stores a collection of elements.
--> The queue operates on first in first out (FIFO) algorithm.
--> A stack is a linear data structure.
--> It follows the last in first out approach.
--> A new item is added at the top of a stack.
--> Both insert and deletion operation is performed from one end of the stack.
--> A Linked List is a data structure.
--> The Linked List is like an array but, the Linked List is not stored sequentially in the memory.
--> Every linked list has 2 parts, the data section and the address section that holds the address of the next element in the list, which is called a node.
Non-linear data structure: Data structures where data elements are not placed sequentially or linearly are called non-linear data structures. In a non-linear data structure, we can’t traverse all the elements in a single run only.
--> A tree is a data structure that has one root node and many sub-nodes.--> It is another one of the data structures which are designed on top of a linked list.
--> A Graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of vertices and edges.
--> The vertices are sometimes also referred to as nodes and the edges are lines or arcs that connect any two nodes in the graph.
--> More formally a Graph is composed of a set of vertices( V ) and a set of edges( E ).
--> The graph is denoted by G(E, V).
Drop a 🌟 if you find this repository useful.
If you have any doubts or suggestions, feel free to reach me.
📫 How to reach me: