เฮโรอีน
 | |
 | |
| ข้อมูลทางคลินิก | |
|---|---|
| ชื่ออื่น | Diacetylmorphine, acetomorphine, (dual) acetylated morphine, morphine diacetate, Diamorphine[3] (BAN UK) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | heroin |
| Dependence liability | สูงมาก[1] |
| Addiction liability | สูงมาก[2] |
| ช่องทางการรับยา | ฉีดเข้าทางหลอดเลือดดำ หายใจเข้า transmucosal ทางปาก พ่นจมูก ไส้ตรง ฉีดเข้ากล้ามเนื้อ ฉีดเข้าชั้นใต้ผิวหนัง ฉีดเข้าช่องไขสันหลัง |
| ประเภทยา | โอปิออยด์ |
| รหัส ATC | |
| กฏหมาย | |
| สถานะตามกฏหมาย |
|
| ข้อมูลเภสัชจลนศาสตร์ | |
| ชีวประสิทธิผล | <35% (ทางปาก), 44–61% (หายใจเข้า)[4] |
| การจับกับโปรตีน | 0% (morphine metabolite 35%) |
| การเปลี่ยนแปลงยา | ตับ |
| ระยะเริ่มออกฤทธิ์ | ภายในไม่กี่นาที[5] |
| ครึ่งชีวิตทางชีวภาพ | 2–3 นาที[6] |
| ระยะเวลาออกฤทธิ์ | 4 ถึง 5 ชั่วโมง[7] |
| การขับออก | 90% ไตในฐานะglucuronide ส่วนน้ำดี |
| ตัวบ่งชี้ | |
| |
| เลขทะเบียน CAS | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.380 |
| ข้อมูลทางกายภาพและเคมี | |
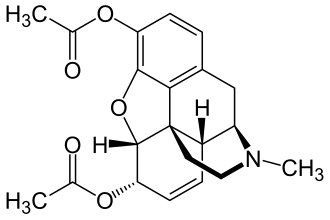
| สูตร | C21H23NO5 |
| มวลต่อโมล | 369.417 g·mol−1 |
| แบบจำลอง 3D (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
เฮโรอีน (อังกฤษ: heroin) มีอีกชื่อว่า ไดอาเซทิลมอร์ฟีน (diacetylmorphine) และ ไดอามอร์ฟีน (diamorphine) กับชื่ออื่น ๆ[3] เป็นโอปิออยด์มีกำลังที่ส่วนใหญ่ใช้ในฐานะยากระตุ้นความบันเทิงที่ก่อให้เกิดอาการเคลิ้มสุข ไดอามอร์ฟีนทางการแพทย์เป็นเกลือไฮโดรคลอไรด์บริสุทธิ์ มีการขายผงขาวและน้ำตาลอย่างผิดกฎหมายจำนวนมากทั่วโลก เนื่องจากเฮโรอีนสามารถ "ตัด" ได้หลายรูปแบบ เฮโรอีนใช้ในทางการแพทย์ในหลายประเทศเพื่อบรรเทาอาการปวด อย่างในช่วงคลอดลูก หรือมีโรคหัวใจวาย เช่นเดียวกันกับการบำบัดทดแทนโอปิออยด์[8][9][10]
ผลข้างเคียงโดยทั่วไปได้แก่การกดการหายใจ (หายใจน้อยลง) ปากแห้ง เซื่องซึม การทำงานทางจิตบกพร่อง ท้องผูก และการติด[11] การใช้งานด้วยวิธีการฉีดสามารถก่อให้เกิดฝี การติดเชื้อที่เยื่อบุหัวใจ เชื้อที่ติดต่อทางเลือด และโรคปอดอักเสบ[11] หลังการใช้งานเป็นเวลายาวนาน อาการที่เกี่ยวกับการหยุดใช้งานโอปิออยด์จะเริ่มมีผลหลังใช้งานครั้งสุดท้ายภายในไม่กี่ชั่วโมง[11] ถ้าฉีดเข้าเส้นเลือด เฮโรอีนจะมีผลมากกว่ามอร์ฟีนในขนาดเดียวกันสองถึงสามเท่า[2] เฮโรอีนมักปรากฏเป็นผงสีขาวหรือน้ำตาล[11]
อ้างอิง
[แก้]- ↑ Bonewit-West K, Hunt SA, Applegate E (2012). Today's Medical Assistant: Clinical and Administrative Procedures (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 571. ISBN 9781455701506.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Heroin". Drugs.com. 18 May 2014. เก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 19 October 2016. สืบค้นเมื่อ 19 October 2016.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Sweetman SC, บ.ก. (2009). Martindale: the complete drug reference (36th ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. p. 42. ISBN 978-0-85369-840-1.
- ↑ Rook EJ, van Ree JM, van den Brink W, Hillebrand MJ, Huitema AD, Hendriks VM, Beijnen JH (January 2006). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of high doses of pharmaceutically prepared heroin, by intravenous or by inhalation route in opioid-dependent patients". Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology. 98 (1): 86–96. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2006.pto_233.x. PMID 16433897.
- ↑ Riviello RJ (2010). Manual of forensic emergency medicine : a guide for clinicians. Sudbury, Mass.: Jones and Bartlett Publishers. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-7637-4462-5. เก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 18 March 2017. สืบค้นเมื่อ 29 August 2017.
- ↑ "Diamorphine Hydrochloride Injection 30 mg – Summary of Product Characteristics". electronic Medicines Compendium. ViroPharma Limited. 24 September 2013. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 30 March 2014. สืบค้นเมื่อ 30 March 2014.
- ↑ Field J (2012). The Textbook of Emergency Cardiovascular Care and CPR. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 447. ISBN 978-1-4698-0162-9. เก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 10 September 2017.
- ↑ Friedrichsdorf SJ, Postier A (2014). "Management of breakthrough pain in children with cancer". Journal of Pain Research. 7: 117–23. doi:10.2147/JPR.S58862. PMC 3953108. PMID 24639603.
- ↑ National Collaborating Centre for Cancer (UK) (May 2012). Opioids in Palliative Care: Safe and Effective Prescribing of Strong Opioids for Pain in Palliative Care of Adults. Cardiff (UK): National Collaborating Centre for Cancer (UK). PMID 23285502.
- ↑ Uchtenhagen AA (March 2011). "Heroin maintenance treatment: from idea to research to practice" (PDF). Drug and Alcohol Review. 30 (2): 130–7. doi:10.1111/j.1465-3362.2010.00266.x. PMID 21375613. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิม (PDF)เมื่อ 28 August 2021. สืบค้นเมื่อ 20 April 2018.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 "DrugFacts—Heroin". National Institute on Drug Abuse. October 2014. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 19 October 2016. สืบค้นเมื่อ 19 October 2016.
แหล่งข้อมูลอื่น
[แก้]- เฮโรอีน ที่เว็บไซต์ Curlie
- NIDA InfoFacts on Heroin
- ONDCP Drug Facts
- U.S. National Library of Medicine: Drug Information Portal – Heroin
- BBC Article entitled 'When Heroin Was Legal'. References to the United Kingdom and the United States
- Drug-poisoning Deaths Involving Heroin: United States, 2000–2013 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics.
- Heroin Trafficking in the United States (2016) by Kristin Finklea, Congressional Research Service.